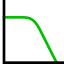
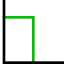
Averaging is useful in situations when the signal of interest is periodic and (random) noise is present on top of it. By taking multiple measurements of the signal and averaging them, the signal to noise ratio will increase.
Properties and actions
To control the behavior of the Average I/O, several properties are available.
These can be accessed through a popup menu which is shown when the I/O is right clicked in the Object screen.
The properties can also be accessed through its settings window which is shown when the I/O is double clicked in the Object screen.
To open the Object screen, click the  Show object screen button.
Show object screen button.
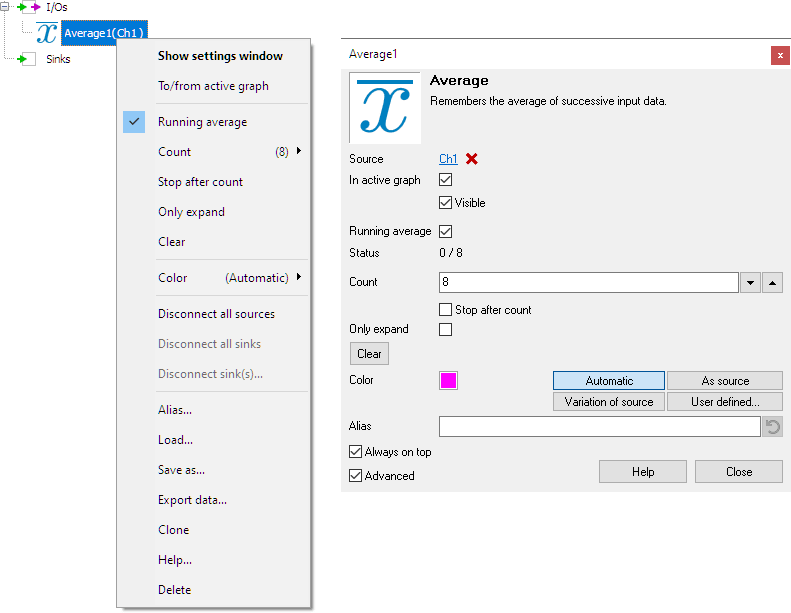
By default, the settings window only shows the most used settings. When Advanced is ticked, the extended window with all settings is shown. See also the program settings.
Count
The Count property determines how many measurements are averaged. Several standard values are available, as well as a user defined setting.
Running average
When the property Running average is switched on, the Average I/O will continuously replace a part of its memory by the newly arriving measurement, effectively "forgetting" the oldest measurement. When switched off, the Average I/O operates in average-of-n mode. The average will then automatically be cleared after n measurements.
Stop after count
When the Stop after count option is checked, the Average I/O will stop collecting data when Averaging count measurements have been collected.
Status
The Status indicator shows how far the Average I/O is in its averaging process.
Only expand
When Only expand is set, the data size of the Average I/O gets higher when the source's data size grows, but does not shrink when the source's data does. This can be useful when averaging data of a source with varying data size.
Clear
The Average I/O can be manually cleared with the Clear action. The internal average count is reset when the Clear action is executed.