A typical application of the Window I/O is to remove spectral leakage in a frequency spectrum using a Fourier Transform. The FFT I/O does have a window function built-in already, therefore using the Window I/O is not required there.
A second application is to shape signal bursts, e.g. to use in the Arbitrary Waveform Generator.
Properties
To control the behavior of the Window I/O, several properties are available.
These can be accessed through a popup menu which is shown when the I/O is right clicked in the Object screen.
The properties can also be accessed through its settings window which is shown when the I/O is double clicked in the Object screen.
To open the Object screen, click the  Show object screen button.
Show object screen button.
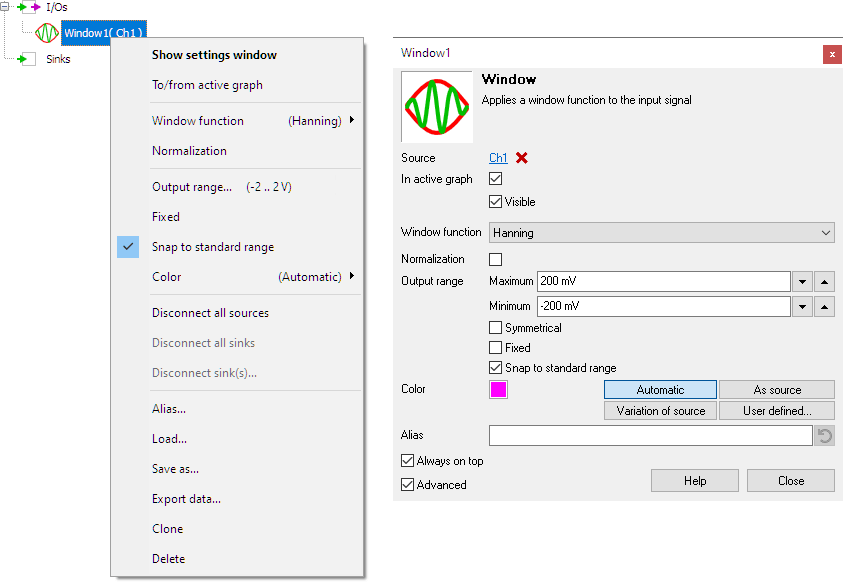
By default, the settings window only shows the most used settings. When Advanced is ticked, the extended window with all settings is shown. See also the program settings.
Window function
The setting Window function defines which algorithm is used to adapt the signal. Several windows functions can be selected from:
- Rectangle
- Hanning
- Hamming
- Bartlett
- Parzen
- Welch
- Blackman
- Blackman-Harris
- Flat top
- Nuttall
- Blackman-Nuttall
The window Rectangle is basically no window, it does not change the signal.
Normalization
A Window function changes the amount of energy in the signal. When performing an FFT on the windowed signal, the magnitudes of the spectral bins will be lower than of a non-windowed signal. To compensate for that, a Normalization can be enabled, which will give the spectral bins the correct magnitudes.