
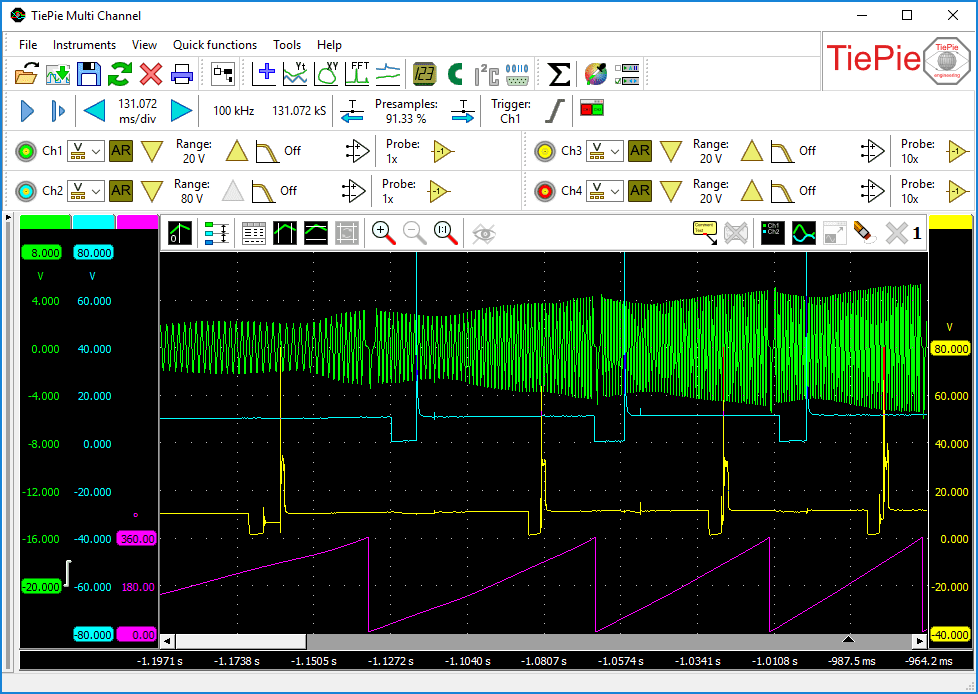
This angle signal can be combined in a graph with an injector signal and/or an ignition signal. Relations between the crankshaft angle and the injection or ignition moments are then immediately visible.
Properties and actions
To control the behavior of the Crankshaft Angle I/O, several properties are available.
These can be accessed through a popup menu which is shown when the I/O is right clicked in the Object screen.
The properties can also be accessed through its settings window which is shown when the I/O is double clicked in the Object screen.
To open the Object screen, click the  Show object screen button.
Show object screen button.
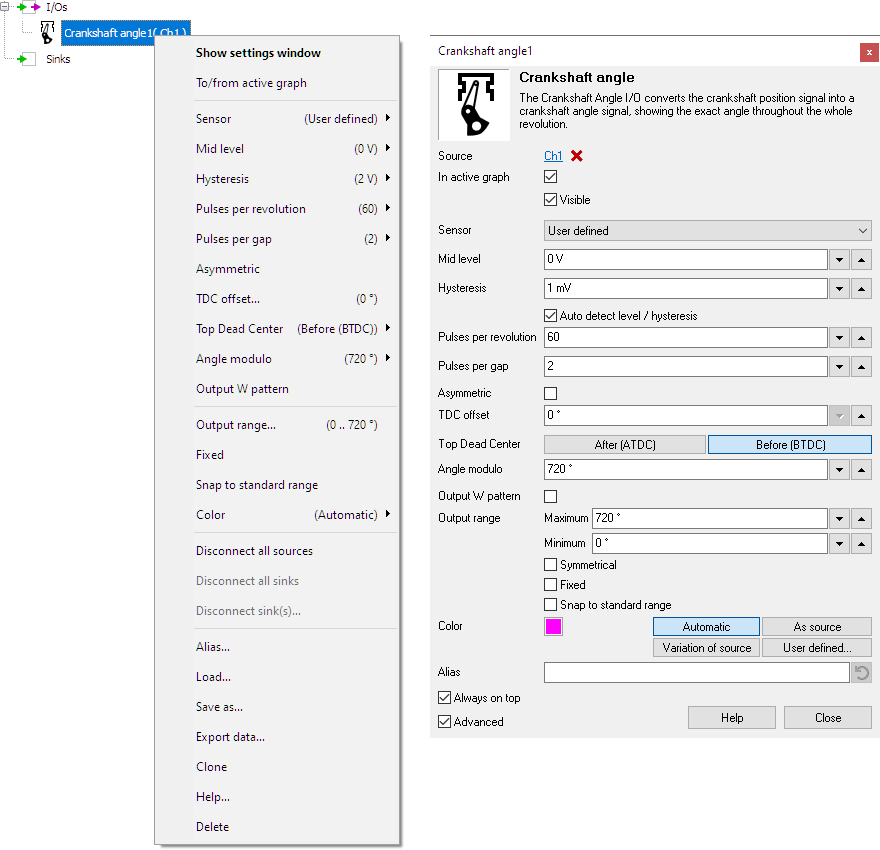
By default, the settings window only shows the most used settings. When Advanced is ticked, the extended window with all settings is shown. See also the program settings.
Sensor
The property Sensor allows to select one of several pre defined common crankshaft sensors. Selecting a pre defined sensor sets other properties like Mid level, Hysteresis, Pulses per revolution and Pulses per gap to the correct values for that sensor.
Mid level
To detect the pulses in the signal, the Crankshaft Angle I/O uses a voltage level to compare the input signal with. The Mid level property sets this level. Some commonly used values can be selected from, as well as a user defined setting.
Hysteresis
For proper detection of the pulses in the signal, the Crankshaft Angle I/O can also use a hysteresis around the Mid level. The property Hysteresis sets it. Some commonly used values can be selected from, as well as a user defined setting.
Auto detect level / hysteresis
When Auto detect level / hysteresis is enabled, the I/O tries to determine the the mid level and a suitable hysteresis automatically.
Pulses per revolution
The Pulses per revolution property must be filled with the number of periods that the crankshaft signal of the used engine produces per revolution. This number must include the "missing" pulses in the gap(s). When multiple gaps per revolution occur, include the number of missing pulses for all gaps.
Several commonly used values can be selected from, a user defined setting is available as well. The default setting is 60 pulses per revolution.
Pulses per gap
The Pulses per gap property must be filled with the number of periods that are "missing" in a gap. When multiple gaps per revolution occur, use the number of missing pulses for one gap.
Several commonly used values can be selected from, a user defined setting is available as well. The default setting is 2 pulses per gap.
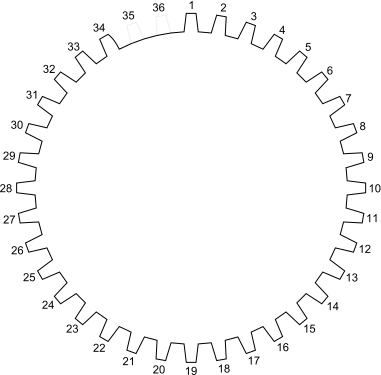
Example with 34 pulses and 1 gap of 2 pulses (36-2):
- Pulses per revolution = 34 + 2 = 36
- Pulses per gap = 2
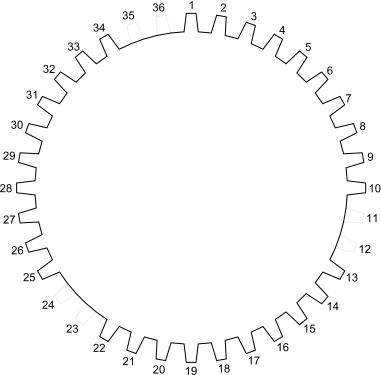
Example with 30 pulses and 3 gaps of each 2 pulses (36-2-2-2):
- Pulses per revolution = 30 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 36
- Pulses per gap = 2
Asymmetric
In order to determine the crankshaft angle as accurate as possible, both the rising edge and the falling edge of a pulse are used. When the pulses of the crankshaft teeth ring are asymmetrical and the used sensor is a Hall type, this may result in incorrect crankshaft angles.
Enable the property Asymmetric to compensate for the asymmetrical pulses and get correct crankshaft angles.
TDC offset
The TDC offset property can be used to compensate the determined crankshaft angle for an engine where the reference gap does not match with Top Dead Center. When the TDC offset is zero, the reference gap is treated as zero degrees for the crankshaft angle.
Top Dead Center
The property Top Dead Center determines how the crankshaft angle is defined:
- Before (BTDC): The angle starts at the value set for Angle modulo and then decreases to zero, indicating the angle before TDC.
- After (ATDC): The angle starts at zero and then increases to the value set for Angle modulo, indicating the angle after TDC.
The default value is Before TDC.
Angle modulo
The Crankshaft Angle I/O converts the crankshaft position sensor signal into an angle signal. When the crankshaft position sensor signal contains more revolutions of the engine, the Crankshaft Angle I/O will accumulate the determined angles of all revolutions. By entering a value in the Angle modulo property, the determined angle will be reset to zero when the entered angle value is reached. Some commonly used values can be selected from, a user defined setting is available as well. The default setting is 720 degrees.
Output W pattern
When the property Output W pattern is enabled, the crankshaft angle will travel up and down between 0 degrees and 180 degrees. The graph will resemble the shape of a "W" and represent the position of a piston traveling in a cylinder.


