When the CAN data contains J1939 messages, these are shown as well. They can be additionally decoded using the J1939 decoder I/O.
When the CAN data contains messages that are compatible with CANopen, exta CANopen related fields are shown as well.
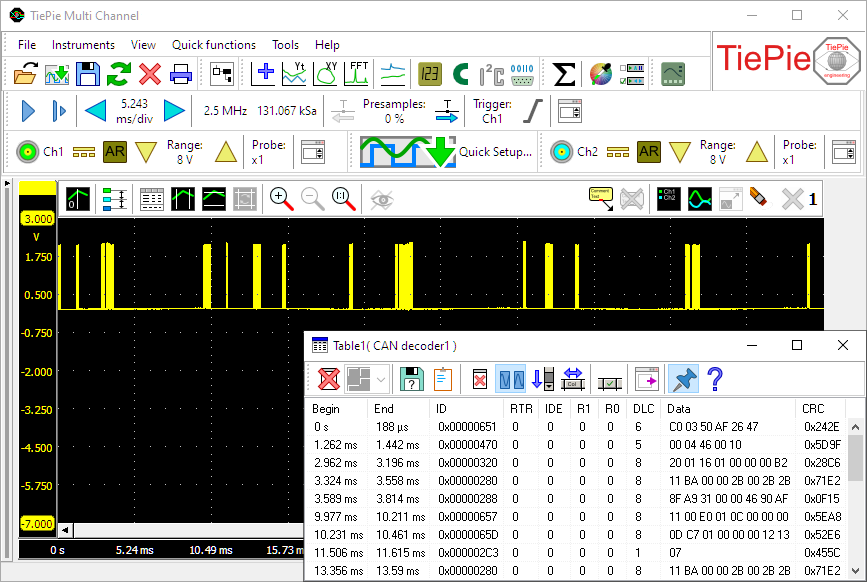
The following fields are extracted from the CAN data by the decoder:
| Protocol | Field name | Purpose | Default shown |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAN | ID | (Unique) identifier for the data | |
| RTR | Remote transmission request: if 1, remote data is requested | ||
| IDE | Identifier extension bit: if 1, the ID consists of 29 instead of 11 bits | ||
| R1 | Reserved bit, only in extended format | ||
| R0 | Reserved bit (it must be set to dominant (0), but accepted as either dominant or recessive) | ||
| DLC | Data length code: number of data bytes (0-8 bytes) | ||
| Data | Transmitted data (length dictated by DLC field) | ||
| CRC | Cyclic redundancy check | ||
| CRC delimiter | Must be recessive (1) | ||
| Ack | Indicates whether the message was acknowledged | ||
| Flags | Indicates errors in the CAN data | ||
| J1939 | Priority | Message priority, provides 8 levels, 0 is highest, 7 is lowest | |
| PGN | Parameter Group Number | ||
| Source address | Source address | ||
| Reserved | Reserved for future use, must now be set to 0 | ||
| Data page | DP, selector for protocol data unit (PDU), currently at 0, page 1 for future purposes | ||
| PDU format | PF, 0-239 indicates destination address in PS, 240-255 indicates extension to PF | ||
| PDU specific | PS, content interpreted according to information in PDU Format | ||
| CANopen | Node ID | Identifies a device on the CANopen bus | |
| Function code | Identifies the CANopen message type | ||
| Object | CANopen communication object type |
To show or hide specific columns from the table, use the Select columns
( ) button
in the Table sink.
) button
in the Table sink.
Double clicking a row in the table will zoom the active graph in to the time frame corresponding to the table row.
An example of decoded CAN data is shown below.
Properties and actions
To control the behavior of the CAN decoder I/O, several properties are available.
These can be accessed through a popup menu which is shown when the I/O is right clicked in the Object screen.
The properties can also be accessed through its settings window which is shown when the I/O is double clicked in the Object screen.
To open the Object screen, click the  Show object screen button.
Show object screen button.
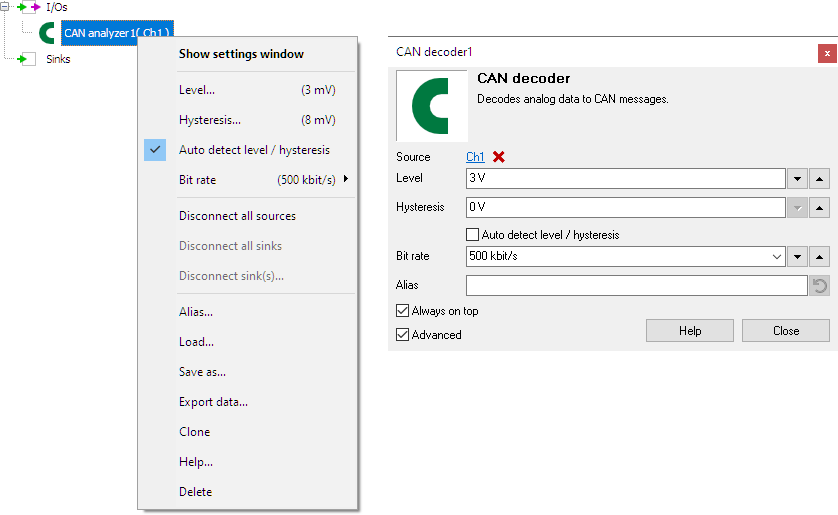
By default, the settings window only shows the most used settings. When Advanced is ticked, the extended window with all settings is shown. See also the program settings.
Level
In order to decode the analog signal into a digital signal, the CAN decoder I/O compares the analog input signal with a mid level: anything above that level is considered "high" and anything below that level is considered "low".
Hysteresis
To minimize the effect of noise on the signal when comparing the signal to the level, a Hysteresis can be used around that level. Anything above "level + hysteresis/2" is considered "high" and anything below "level - hysteresis/2" is considered "low".
Auto detect level and hysteresis
Enabling Auto detect level and hysteresis will let the software determine a suitable mid level and hysteresis, based on the measured signal. Each time new data is available, the suitable level and hysteresis will be determined again. In streaming mode, level and hysteresis are determined once based on the first chunk of data and remain at these values though out the whole measurement.
Auto detect level and hysteresis is default enabled.
Bit rate
For correct detection, the Bit rate property must be set to the correct value corresponding to the bus that is under measurement. It can be set to several common values, but also to a user defined value.