The EMI I/O adds a new toolbar to the user interface of the software with all relevant settings. Additionally it gives access to four standard limit lines (EN61326-1:2006 / EN55011:2007) that can be added to the graph for easy comparison.
The EMI I/O has five output signals that can be shown in a graph:
- Frequency spectrum: the defined frequency spectrum of the measured input signal
- Group 1 Class A Radiated Emissions limit: Class A limit line according to EN55011:2016
- Group 1 Class B Radiated Emissions limit: Class B limit line according to EN55011:2016
- Group 2 Class A Radiated Emissions limit: Class A limit line according to EN55011:2016
- Group 2 Class B Radiated Emissions limit: Class B limit line according to EN55011:2016
The EMI I/O can only be used in combination with the following instruments:
- Handyscope HS6 DIFF - 1000XMEG
- Handyscope HS6 DIFF - 1000XMESG
- Handyscope HS6 DIFF - 1000XMEG-W5
- Handyscope HS6 DIFF - 1000XMESG-W5
- WiFiScope WS6 DIFF - 1000XMSG
- WiFiScope WS6 DIFF - 1000XMESG
- WiFiScope WS6 DIFF - 1000XMEG-W5
- WiFiScope WS6 DIFF - 1000XMESG-W5
- WiFiScope WS6 - 1000XME
- WiFiScope WS6 - 1000XMES
- WiFiScope WS6 - 1000XME-W5
- WiFiScope WS6 - 1000XMES-W5
Only one channel of an instrument with option E can be connected to an EMI I/O.
Properties and actions
To control the behavior of the EMI I/O, several properties and actions are available. These can be accessed through a popup menu which is shown when the I/O is right clicked.

The EMI I/O also adds a new toolbar with all relevant settings to the user interface of the software.
Continuous
One shot
Mode
The EMI I/O supports three operating modes:

Clear

Input range
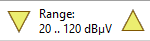
- 0 .. 100 dBµV
- 20 .. 120 dBµV
- 40 .. 140 dBµV
When the Unit is changed, the input ranges change accordingly.
Unit

- dB
- dBV
- dBmV
- dBµV
- dBµV/m (at 10m)
- dBm
When changing the unit, the axis of the graph changes accordingly, as well as the input ranges.
Minimum frequency

Maximum frequency
Zooming
Via the toolbar various horizontal zoom actions can be selected from:


Resolution bandwidth

Window function

To minimize the effect of spectral leakage, the input record of the FFT can be multiplied with a Window. This is called windowing. Several windows can be chosen in the menu of the FFT I/O, which all basically perform the same action: they make the edges of the record smoother to make the discontinuities smaller. In most cases, the Flat top window or the Blackman-Harris window will give the best results. However, if your data contains an integer number of cycles, no discontinuities will occur and the rectangle (no windowing) window will give the best result. The following window functions are available for the FFT-block:
- Rectangle
- Hanning
- Hamming
- Bartlett
- Parzen
- Welch
- Blackman
- Blackman-Harris
- Flat top
The default selected windows is Flat top.
Antenna attenuation

The default value is 0 dB (no attenuation).
Probe attenuation
The default value is 0 dB (no attenuation).
Limit lines
Two limit lines according to EN61326-1:2006 / EN55011:2007 can be shown in the spectrum graph:


ADC Spur compensation.
The ADC used in the instrument causes small spurs at specific frequencies in the spectrum. These spurs are small and far within the specifications of the instrument, but due to the high accuracy spectrum that is generated, they can be visible. By enabling the property ADC spur compensation they can be filtered out of the spectrum. This may affect actual frequency components at the same frequencies in your measured signal, which will then be displayed with a wrong magnitude.
ADC spur compensation is default enabled.